Why are they called wisdom teeth?
Wisdom teeth normally erupt between the ages of 16-20, in line with a person’s physical maturity.
Theoretically, a person should be wiser and that is why they were given the name “wisdom teeth”.
These teeth are the last ones to erupt.
How many wisdom teeth do we have?
Generally, people have four wisdom teeth: two on the upper jaw and two on the lower jaw. These teeth grow at the very back of the upper and lower jawbones and are known as the third molar.
Does everyone have wisdom teeth?
Not everyone has wisdom teeth. These teeth are disappearing according to the experts. New generations have different genes, which is excluding these teeth. It is claimed that this happens because we are increasing our consumption of softer food. Therefore, chewing is much easier. This can also be due to the natural evolution of the species.
What are impacted wisdom teeth?
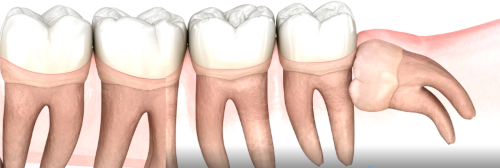
Teeth are impacted when they fail to erupt through the gums. As the last teeth to grow, the other 28 teeth are already occupying the available space on the dental arch and, not having enough space, they remain submerged below the gum.
Should you have your wisdom teeth removed?
- If the tooth is severely damaged or causing too much pain, it should be extracted. Root canal treatment is not recommended.
- Correct positioning on the dental arch is very important. If they are facing your cheekbone, or in other words are incorrectly positioned, they may cause bruising and pain.
- Regardless of whether they cause pain, if any of the wisdom teeth creates a cavity in an adjacent tooth, it should be extracted.
- The tissues around the wisdom teeth can develop cysts or tumours and this can be another reason for removing them.
- Sometimes in orthodontic treatments, it is necessary to remove the wisdom teeth to create more space and correct the positioning of the teeth.
People assume that if an impacted wisdom tooth does not hurt, they should not be concerned about them. This is not quite the case. A maxillofacial surgeon should monitor these teeth. He will assess the existence or possibility of diseases based on the tissue quality around them. These teeth require special attention, annual checks, and x-rays. The majority of dentists agree that if a healthy wisdom tooth is not causing pain, gum problems, or damaging other teeth, it should not be removed.
Are there any adverse effects related to wisdom teeth removal?
- Age will affect healing time and recovery will be more difficult, because the root of the tooth is larger.
- If there are infections or abscesses, they should be treated beforehand.
- Occasionally, wisdom teeth may be too close to the inferior dental nerve and its extraction can damage the adjacent structure. In this case, monitoring is the ideal solution and removal should only be used as a last resort.
What can I expect from wisdom tooth surgery?
If removal is recommended, the patient will be sent to an appointment with an expert in maxillofacial surgery. You will be asked questions regarding medication that you may be taking and systemic diseases. Wisdom tooth removal is performed in the dentist office under local anaesthesia. It is a painless procedure. Potential arising issues may be related to the position of the tooth on the gum and the size of its roots. In younger patients, this surgery is easier.
After the removal, is there any special care?
After surgery, you may feel some discomfort. Swelling, particularly in the cheek area, is common and can be relieved with ice packs. You should take the prescribed medication, usually an antibiotic for complex wisdom tooth extractions (semi-impacted or impacted). It is a surgery after all. Also, you may have to adapt your eating habits on the day of the surgery and the following day by eating soft and cold foods.
Many people have impacted wisdom teeth for years and they are not aware of it. These teeth grow, do not erupt, and stay submerged below the gums. Since it is not visible, if it does not cause pain or discomfort, the person will not feel or be aware of its existence. It is not unusual to find our patients surprised when telling them about the existence of an impacted wisdom tooth. Orthopantomogram or maxillary x-rays make this finding possible.

