Bacterial plaque is a sticky, colourless film that constantly forms on your teeth and gums and consists of bacteria and its products. It is the main cause of tooth decay and periodontal diseases that may result in tooth loss.
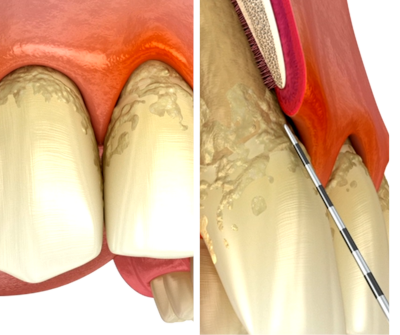
At first, this film has a soft texture and, if not removed at this stage, it hardens into a rough deposit called tartar.
Tartar removal requires a set of clinical procedures (scaling and root planing and others) performed by health professionals.
How to identify bacterial plaque?
Everyone can have bacterial plaque.
Bacteria are constantly being created in our mouths. To grow, these bacteria use ingredients found in our diet and saliva. Bacterial plaque together with carbohydrates (especially sugar) produces acid that will attack the hard tissues of a tooth (enamel and dentine). Thus, there is acid production whenever sugary foods or drinks are consumed.
After frequently being attacked by these acids, the enamel deteriorates and tooth decay will appear. If not removed, bacterial plaque may also cause gum inflammation, which results in gingivitis (red, swollen and bleeding gums).
There are products such as plaque disclosing agents, which ‘give’ colour. By using this product, it will be possible to see where the plaque is and correct the methods of oral hygiene.
How to prevent plaque formation?
The formation is a constant process in our mouth. However, we can prevent plaque build-up and its consequences. Ensure that:
- You carefully brush all surfaces of the teeth at least two times a day;
- You use dental floss daily to remove the plaque build-up between the grooves of teeth and gums;
- You are careful with sugary foods and drinks (cakes, cookies, chocolate bread, chips, sodas, etc.) as they facilitate bacterial adherence to the tooth surface by producing acids, which results in the destruction of the teeth.
- If necessary, there are widely-used antibacterial agents (such as chlorhexidine) that through mouthwash or toothpaste are highly effective against bacterial plaque formation. Also act as good removal agents. Please consult with your health professional.
Reviewed by VitaCentre Dental Clinic Staff on June 1, 2023

